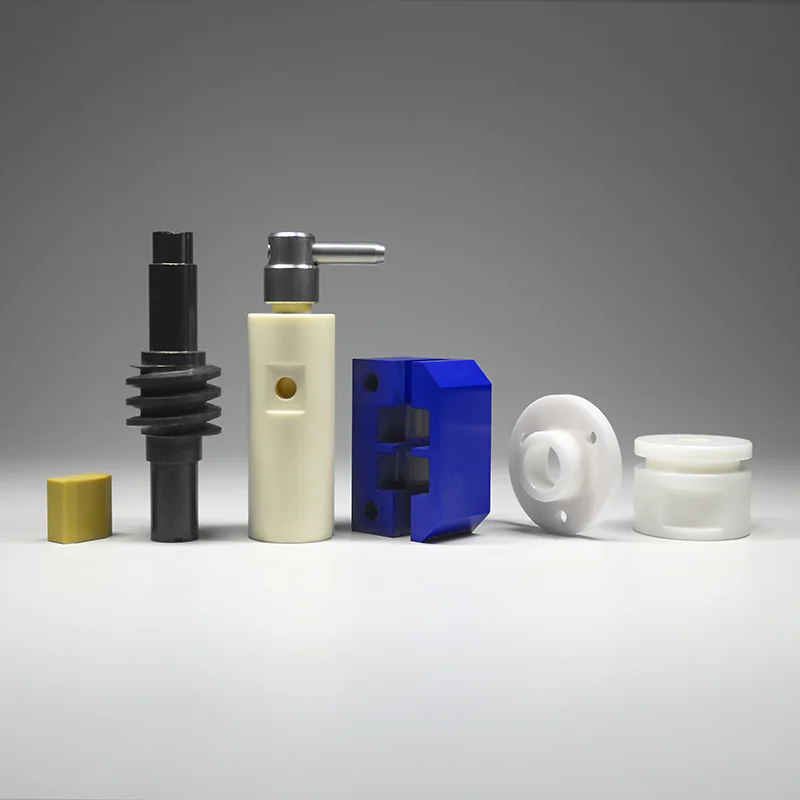
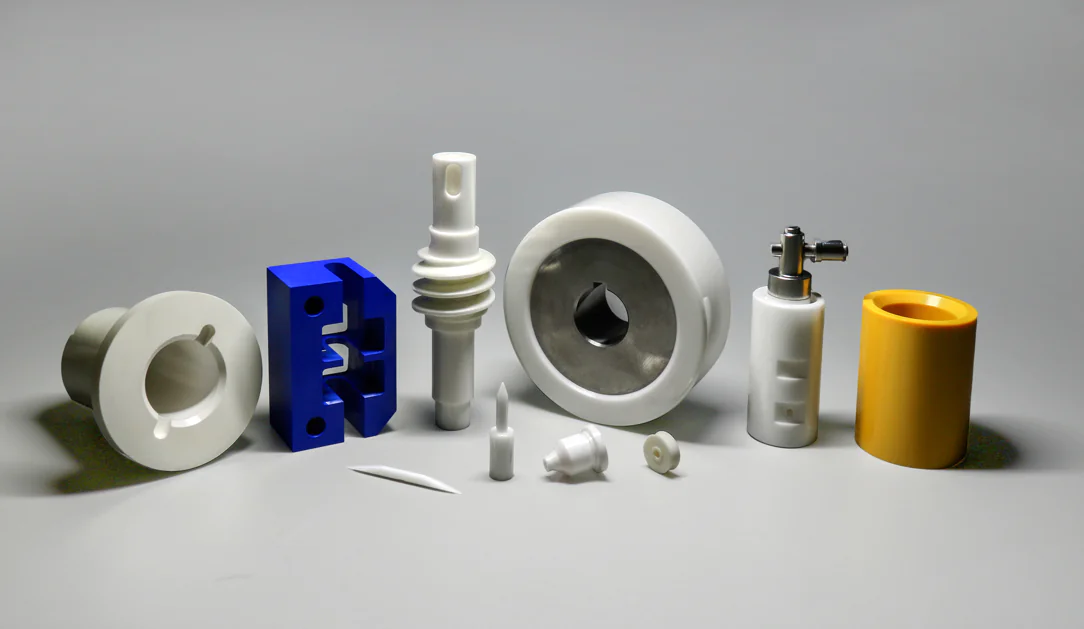
첨단 세라믹: 고대 공예에서 첨단 핵심 소재로의 놀라운 변신
1.1 전통 도자기의 한계와 돌파구
Traditional ceramics, crafted from clay and fired at high temperatures, have long been valued for their heat resistance and corrosion stability. Yet their inherent limitations—extreme brittleness and low mechanical strength—have left them ill-equipped to meet the rigorous demands of today’s high-tech industries. For example, in aerospace, conventional ceramics fail to withstand the thermal shock and mechanical stress of rocket engines, while in medical applications, their poor biocompatibility restricts use in critical implants where reliability and tissue integration are non-negotiable. These gaps have driven the evolution of advanced ceramics, which overcome historic flaws through precise material engineering and innovative manufacturing.

1.2 첨단 세라믹의 등장
Advanced ceramics deliver dramatic performance gains by leveraging high-purity raw materials and tightly controlled manufacturing workflows. For example, zirconia ceramics are now the gold standard for artificial joints and dental restorations, thanks to their exceptional wear resistance and biocompatibility that closely mimics human tissue. Silicon carbide ceramics, meanwhile, exhibit unparalleled oxidation resistance at extreme temperatures, providing critical protection for aerospace engine components under thermal stress. By engineering nanostructures, these materials achieve a perfect balance of hardness and toughness, embodying the engineering principle of “structural integrity and functional consistency.”
1.3 고급 세라믹의 분류 및 특성
Advanced ceramics are categorized by chemical composition into three primary groups:
- Oxide ceramics (e.g., alumina, zirconia): Boast extreme hardness, high melting points, and superior corrosion resistance, ideal for industrial wear parts and medical implants.
- Nitride ceramics (e.g., silicon nitride, aluminum nitride): Offer high mechanical strength, enhanced fracture toughness, and outstanding thermal stability, critical for high-speed cutting tools and electronic substrates.
- Carbide ceramics (e.g., silicon carbide, boron carbide): Feature exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and chemical inertness, used in armor plating and abrasive components.
These tailored properties position advanced ceramics as a cornerstone material across industries from healthcare to aerospace.
II. 애플리케이션 시나리오: 산업 생태계 재편
2.1 의료 분야: 정밀도 및 개인화
Advanced ceramics are revolutionizing modern healthcare, with zirconia ceramics leading the way in dental implants and restorations. Their optical translucency and biocompatibility enable natural-looking, long-lasting solutions that drive the shift toward precision dentistry. Additionally, bioresorbable bioceramics have unlocked breakthroughs in implantable devices—such as degradable bone screws and plates—that eliminate the need for secondary surgery, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.

2.2 에너지 부문: 안전과 효율성의 균형
Advanced ceramics are pivotal to the global energy transition, with silicon nitride ceramics dramatically improving lithium-ion battery safety by enhancing thermal stability and extending cycle life. Solid oxide fuel cells and ceramic-enhanced solar cells also leverage these materials’ high efficiency and durability to accelerate the shift away from fossil fuels. As demand for clean energy grows, advanced ceramics will play an increasingly critical role in building a sustainable energy infrastructure.
2.3 지능형 시스템: 기계-전기 에너지 변환
Piezoelectric ceramics are the backbone of modern sensor and actuator technology, converting mechanical force into electrical signals with high precision. In smartphones, piezoelectric sensors deliver responsive haptic feedback that elevates the user experience, while in industrial automation, piezoelectric actuators enable sub-micron motion control to boost production accuracy. As IoT and smart manufacturing expand, the demand for these ceramic components will surge.
2.4 항공우주 공학: 극한 환경에서의 신뢰성
In aerospace, where failure is not an option, advanced ceramics provide unmatched performance. Silicon carbide ceramics resist high-temperature oxidation, making them essential for turbine and propulsion system components. Silicon nitride ceramics, with their exceptional strength and fracture toughness, are used in critical aircraft structural parts to withstand extreme thermal and mechanical loads. These materials ensure aerospace systems remain reliable even in the harshest conditions.

III. 문화적 연속성: 기술과 전통 장인정신의 통합
3.1 전통 기법의 현대적 해석
Today’s ceramic engineers are reviving the ancient philosophy of “structural and aesthetic consistency”—exemplified by Jingdezhen’s marbled porcelain—through advanced design and manufacturing. Digital fabrication techniques like 3D printing allow for high-fidelity reproduction of classic patterns, while the Jingdezhen Ceramic Gene Bank bridges historical formulations with modern materials science, validating Joseph Needham’s observation that “porcelain represents the fusion of art and industry.”
3.2 기술과 예술적 표현의 융합
Beyond their technical prowess, advanced ceramics offer unique artistic potential. Nanoscale structural tuning enables precise control over color, gloss, and texture, allowing these materials to mimic natural stone or wood in architectural facades. This blend of aesthetics and durability is transforming building design, creating surfaces that are both visually striking and long-lasting.
3.3 장인 정신의 보존과 혁신
The evolution of advanced ceramics is breathing new life into traditional craftsmanship. Modern manufacturing technologies like CNC machining and slip casting allow traditional techniques to be scaled for mass production, improving quality consistency while preserving cultural heritage. Conversely, the artistic richness of traditional ceramics continues to inspire innovative designs in advanced ceramic development, creating a virtuous cycle of preservation and progress.
IV. 향후 전망: 친환경 및 지능형 제조를 향하여
4.1 사용자 지정 및 확장 가능한 프로덕션
Ceramic 3D printing technology is democratizing customization, enabling the production of complex geometries and microstructures with micron-level precision. This breakthrough is unlocking tailored solutions in healthcare, aerospace, and electronics, while advances in large-scale sintering are driving down costs to accelerate widespread adoption. The future of ceramics lies in balancing personalized design with efficient, high-volume production.

4.2 바이오세라믹 및 이식형 장치
Bioresorbable bioceramics are redefining implantable medical technology, with devices like degradable bone fixation implants that gradually dissolve in the body, eliminating the need for follow-up surgery. Beyond orthopedics, bioceramics are being explored in tissue engineering to create artificial skin and vascular grafts, offering new hope for patients with chronic conditions. As research progresses, these materials will become integral to regenerative medicine.
4.3 자가 치유 세라믹과 지속 가능한 인프라
Self-healing ceramics are set to transform infrastructure sustainability by embedding microcapsules or vascular networks that autonomously repair cracks. In construction, these materials can seal fissures in walls and floors, extending structural lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. As cities aim for carbon neutrality, self-healing ceramics will play a key role in building resilient, low-maintenance infrastructure.
4.4 친환경 제조 및 탄소 중립성
Driven by global net-zero goals, low-temperature sintering technologies are revolutionizing ceramic production by cutting energy use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This shift to eco-friendly manufacturing, combined with the deployment of advanced ceramics in solar panels and fuel cells, is accelerating the decarbonization of the industrial sector. The ceramic industry is now a critical player in the fight against climate change.
V. 결론
Advanced ceramics represent the ultimate fusion of scientific innovation and cultural heritage, delivering value across materials science, industrial applications, and cultural preservation. The transition from traditional to advanced ceramics has not only boosted performance but also transformed entire industries, from healthcare to aerospace. Looking ahead, green and intelligent manufacturing will expand their role in personalized medicine, regenerative technologies, and self-sustaining infrastructure, cementing advanced ceramics as a cornerstone of a sustainable future.